Extra- and ordinary beam
Jones matrix
Conoscopic imaging
Crystalline quartz
Iceland Spar (Calcite)
Quarter and half wave plate
Pockels Cell
PE-0100 Double Refraction of Light
Topics:
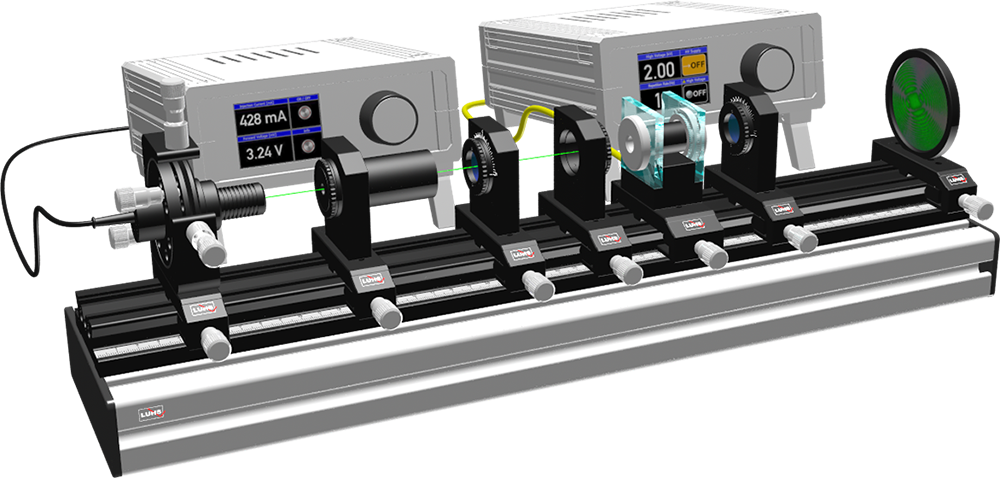
PE-0100 Double Refraction of Light - Setup with a Pockels Cell
Erasmus Bartholin was the first one who reported his observation on double refraction in 1669. He investigated a crystal of calcite: not the only crystal which shows double refraction, but a crystal with an extraordinary high markedness of this phenomenon. His discovery and its first scientific explanation by Christian Huygens in 1674 marked the beginning of the studies on optical crystal properties.
More than 100 years later crystal optics got new impulses through Dominique Arago, who studied the polarization and optical activity, and Jean-Baptiste Biot who defined the first principles of crystal optics, by differentiating in particular uni-axial and bi-axial crystals - principles which are still valid today. Birefringent materials are important components in optics, for example as half- and quarter-wave plates or as Lyot filters to tune laser lines. Double refraction or birefringence can also be induced in crystal like polymers by external electrical fields or stress. The experiments may start with the observation of birefringence shown by calcite crystal. The green probe laser is directed to the calcite and the splitting of the laser beam in ordinary and extraordinary rays are observed. The polarization of these rays is measured by using the rotary polarization analyser. As an example of a biaxial crystal a Pockels cell containing a Lithium Niobate crystal is used and in a conoscopic set-up impressive interference pattern are created when the high voltage is applied. Furthermore the optical retardation for different voltage levels is measured and the so called halve wave voltage determined.
In this experiment we are using a laser emitting a wavelength of 532 nm (green). The light passes the first polarizer. A focusing lens creates the “conical” light beam which traverses the birefringent material. The second polarizer is aligned orthogonally to the first one. In direction of the optical axis, the material behaves isotropic and there will be no change in the polarization stage of the incident light. The corresponding image on the screen remains dark. All other rays propagating inclined to the optical axis undergo a change to their polarization in such a way, that a fraction can pass the orthogonally oriented polarizer. Consequently, a typical intensity distribution results which is a fingerprint for the specific birefringent material. Areas with same intensity (same retardation) are termed as isogyres, places of same birefringence. Conoscopy is a very important method to find the optical axis of raw crystals in optic manufacturing as well as quality control for LCD displays.
| Item | Code | Qty. | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DC-0020 | 1 | LED and Photodiode Controller |
| 2 | DC-0250 | 1 | Active SiPIN Photodetector |
| 3 | LQ-0020 | 1 | Green (532 nm) DPSSL in ø25 housing |
| 4 | MM-0020 | 3 | Mounting plate C25 on carrier MG20 |
| 5 | MM-0024 | 3 | Mounting plate C25-S on carrier MG20 |
| 6 | MM-0110 | 1 | Translucent screen on carrier MG20 |
| 7 | MM-0420 | 1 | Four axes kinematic mount on carrier MG20 |
| 8 | MP-0150 | 1 | Optical Bench MG-65, 500 mm |
| 9 | OC-0040 | 1 | Plano-convex lens f=40 mm in C25 mount |
| 10 | OC-0360 | 1 | Beam Expander x6 in ø25 housing |
| 11 | OC-0710 | 2 | Polarizer in C25 mount |
| 12 | OC-0820 | 1 | Calcite crystal on rod and carrier |
| 13 | OC-0830 | 1 | Optical quartz plate in C25 mount |
| 14 | OC-0840 | 1 | Quarter-wave plate in C25 mount |
| 15 | UM-PE01 | 1 | Manual Double Refraction of Light |
| Option (order separately) | |||
| 16 | DC-0360 | 1 | Pockels Cell HV Driver, digital |
| 17 | OM-0030 | 1 | Pockels Cell 19 mm |
| Media Type | Title | File Size [MBytes] | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| UM-PE01 Double Refraction of Light under creation |
|||
| Catalogue Page | |||
| JPEG, PNG, SVG | Pictures | ||
| MP4 | Video |